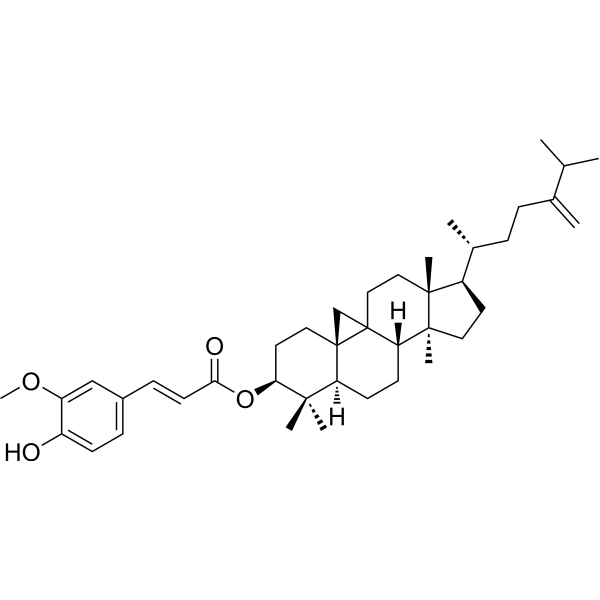
24-Methylene cycloartanyl ferulate
CAS No. 469-36-3
24-Methylene cycloartanyl ferulate( —— )
Catalog No. M32244 CAS No. 469-36-3
24-Methylenecycloartanyl ferulate, a compound belonging to the γ-oryzanol family, demonstrates the ability to enhance parvin-beta expression within human breast cancer cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 268 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name24-Methylene cycloartanyl ferulate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description24-Methylenecycloartanyl ferulate, a compound belonging to the γ-oryzanol family, demonstrates the ability to enhance parvin-beta expression within human breast cancer cells.
-
Description24-Methylenecycloartanyl ferulate, a compound belonging to the γ-oryzanol family, demonstrates the ability to enhance parvin-beta expression within human breast cancer cells. Furthermore, it exhibits potential as an ATP-competitive Akt1 inhibitor, with an EC 50 value of 33.3 μM.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number469-36-3
-
Formula Weight616.91
-
Molecular FormulaC41H60O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 12.5 mg/mL (20.26 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
NSC 122393
NSC 122393 is a fluorescent dye that inhibits the interaction between Bax and Bcl-X and induces apoptosis in Bcl-X overexpressing breast cancer cells.
-
TBMP
TBMP is the viral envelope protein hemagglutinin (HA)-mediated entry novel inhibitor.
-
Cbl-b-IN-5
Cbl-b-IN-5 is a potent CPL-B inhibitor with IC50 values between 3 and 10 μM. Cbl-b-IN-5 has been used to study cancer and diseases related to the immune system.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


